
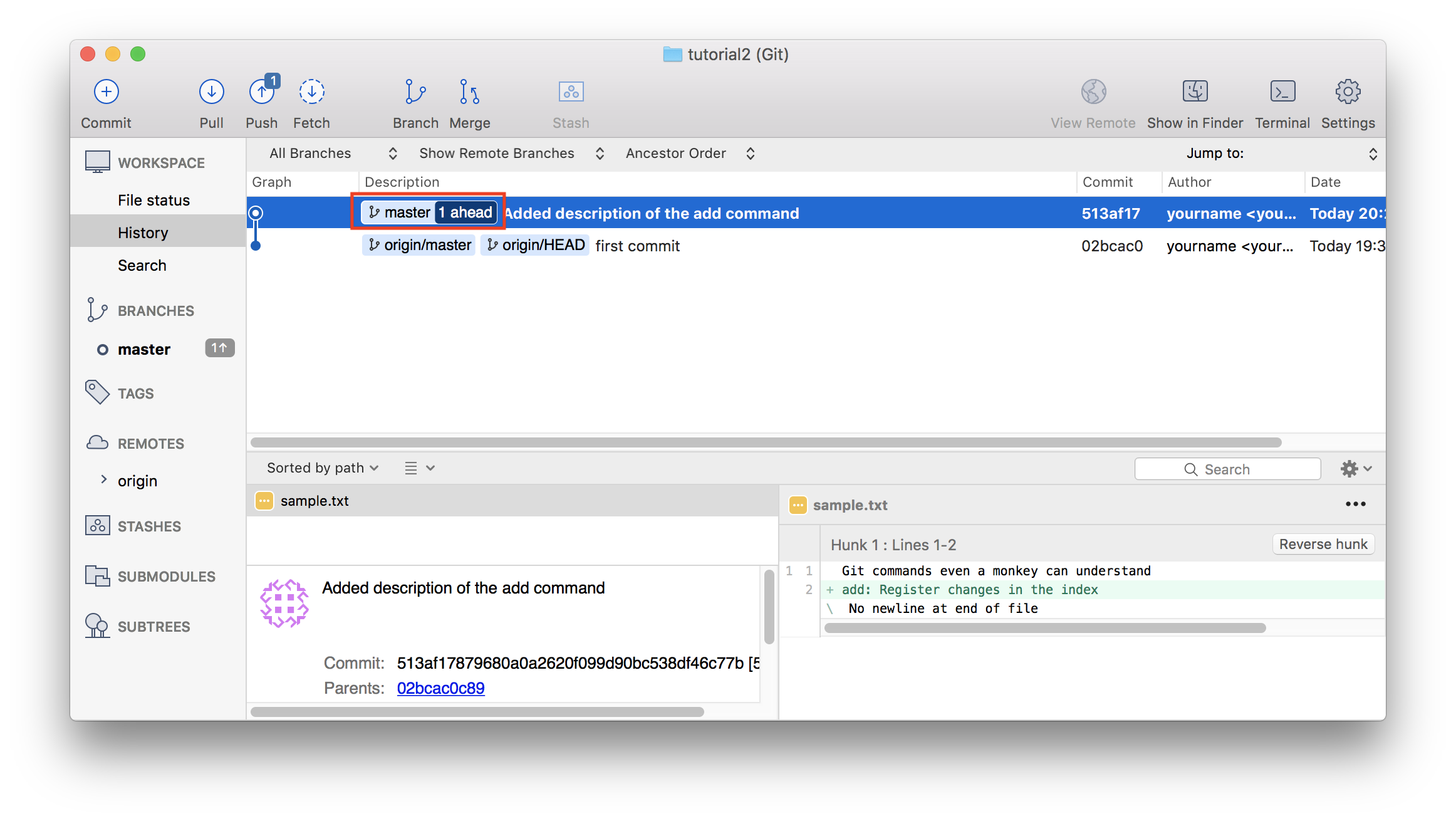
Having successfully added a remote repository, this command will push the contents of your local repository up to the remote repository: git push name-of-repo master.

The most important step for distributing your Git project is to establish a remote server location.
#GIT ADD REMOTE FOR CLONED DIRECTORY HOW TO#
How to Add a Remote Repository to your Server Using Git This exact use case is detailed completely in our full guide on how to publish files with Git. In this case, we will be using the Git “Push” command. With Git, you can manage the files locally, commit changes, and upload the changes without ever leaving a single command line. This can be very helpful if you want to host files that others will need to have access to, and thus require the latest version with most recent changes applied. Using Git as a publishing vehicle can allow for easy file transfer and also allow others to use your project files.
#GIT ADD REMOTE FOR CLONED DIRECTORY INSTALL#
For some users, managing a private server location provides more attractive options as far as customization goes.īe sure to check out our full guide on how to install Git, if you have not completed that step yet. In this example, of course, we will be using an InMotion Hosting server to demonstrate setting up your remote repository with Git.Īs stated before in the Introduction to Git, there are free Git platforms available on the web, but you are forced to use their resources and follow their rules. You can accomplish this by “pushing” and “pulling” content to and from a remote server locations. You can use Git locally to manage file versions, but more power comes when you distribute your work and allows other to collaborate.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
